Schedule a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Understanding Excessive Sweating
The human body’s natural cooling mechanism is a complex process involving multiple physiological systems, and one of its many functions is to regulate _temperature_ through sweating. However, in some individuals, this process can become dysregulated, leading to excessive sweating, also known as **Hyperhidrosis**.
Hyperhidrosis is a common condition characterized by abnormally high levels of sweat production, often accompanied by feelings of embarrassment, anxiety, and social isolation. There are two main types of hyperhidrosis: Generalized Hyperhidrosis, which affects the underarms, palms, and soles of the feet, and Focal Hyperhidrosis, which affects specific areas such as the face.
The exact causes of hyperhidrosis are not fully understood, but research suggests that it is often linked to an overactive _sympathetic nervous system_, which regulates the body’s “fight or flight” response. This system can lead to increased sweat gland activity, resulting in excessive sweating.
Another factor contributing to hyperhidrosis is _genetics_. Individuals with a family history of hyperhidrosis are more likely to develop the condition, and certain genetic variants have been identified that increase the risk of developing hyperhidrosis.
The sweat glands themselves also play a crucial role in hyperhidrosis. In individuals with this condition, sweat glands produce an excessive amount of sweat, which can lead to clogged pores and secondary infections.
In terms of facial hyperhidrosis, the condition is often characterized by excessive sweating on the forehead, _cheekbones_, and around the mouth. This type of hyperhidrosis can be particularly distressing for individuals who experience it, as it can interfere with their daily lives and social interactions.
Botox injections have emerged as a popular treatment option for facial hyperhidrosis. The mechanism behind this treatment is based on toxic botulinum protein, which temporarily paralyzes the _sweat glands_ in the affected area, reducing sweat production and alleviating symptoms.
The efficacy of Botox in treating hyperhidrosis has been extensively studied, with numerous clinical trials demonstrating its safety and effectiveness. Studies have shown that Botox injections can reduce sweating by up to 70%, providing significant relief for individuals suffering from facial hyperhidrosis.
While Botox is a highly effective treatment option for facial hyperhidrosis, it’s essential to note that it may not completely eliminate excessive sweating. However, with repeated injections and proper maintenance, many individuals experience long-term relief from their symptoms.
Other treatment options for facial hyperhidrosis include iodine-based treatments, which work by inhibiting the activity of the sweat glands, and oral medications such as anticholinergic agents, which can help regulate sweat gland function. In severe cases, surgery may be considered as a last resort.
In conclusion, hyperhidrosis is a complex condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, causing significant distress and impairment in daily life. By understanding the science behind this condition, including the role of genetics, the sympathetic nervous system, and sweat glands, we can better appreciate the potential for effective treatments, such as Botox injections.
Hypersweat, also known as hyperhidrosis, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s characterized by excessive sweating, often in specific areas of the body, such as the hands, feet, or face.
The exact causes of hyperhidrosis are still not fully understood, but it’s believed to be related to overactive sweat glands, genetics, and certain medical conditions. In some cases, hyperhidrosis can be triggered by stress, anxiety, or certain medications.
There are several types of hyperhidrosis, including:
- Focal hyperhidrosis: Excessive sweating in a specific area of the body, such as the hands or feet.
- Palmar and plantar hyperhidrosis: Excessive sweating in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
- Craniofacial hyperhidrosis: Excessive sweating in the face and head area.
- Generalized hyperhidrosis: Excessive sweating all over the body.
In people with hyperhidrosis, sweat glands produce an abnormal amount of sweat, leading to excessive perspiration. This can be particularly problematic for individuals who engage in sports or work in environments where sweating is a concern.
Facial hyperhidrosis, in particular, can be embarrassing and affect a person’s self-confidence. Excessive sweating on the face can lead to discomfort, anxiety, and social avoidance.
Botox injections have been shown to be effective in treating excessive sweating of the face and underarms. Botox works by temporarily blocking nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands, reducing the amount of sweat produced.
The procedure involves injecting a small amount of Botox into the affected area. The effects typically last for several months before the body breaks down the toxin, requiring repeated treatments.
Studies have shown that Botox is effective in treating facial hyperhidrosis, with significant reductions in sweat production and improvement in quality of life. However, it’s essential to note that Botox is not a cure for hyperhidrosis and may require ongoing treatment.
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends Botox as a treatment option for facial hyperhidrosis, particularly for individuals who have tried other treatments without success. However, Botox should only be administered by a qualified healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or anesthesiologist.
Before undergoing Botox treatment, it’s essential to consult with a doctor to discuss your individual needs and determine if Botox is the right treatment option for you. You’ll also need to undergo a thorough medical evaluation to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to your excessive sweating.
Additionally, it’s crucial to follow post-treatment instructions carefully to ensure optimal results and minimize potential side effects. This may include avoiding strenuous exercise or hot showers for a few days after treatment.
Overall, while Botox is not a solution for everyone, it can be an effective treatment option for individuals with facial hyperhidrosis who have tried other methods without success. By understanding the condition and discussing treatment options with a qualified healthcare professional, individuals can take control of their excessive sweating and improve their overall quality of life.
No treatment can completely eliminate excessive sweating, but there are several effective options available to manage its symptoms and improve quality of life.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, hyperhidrosis affects approximately 2.8% of the population worldwide (Jampol et al., 2017). This condition is characterized by excessive sweating that can occur in any area of the body, but most commonly affects the underarms, palms, soles, and face.
Hyperhidrosis can be further categorized into two types: primary and secondary. Primary hyperhidrosis is the most common type, accounting for about 80-90% of cases, and is characterized by excessive sweating without any identifiable cause or underlying medical condition.
Secondary hyperhidrosis, on the other hand, is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as hypothyroidism, menopause, medication side effects, or a neurological disorder. In these cases, the sweating can be a symptom of another health issue that needs to be addressed before treatment for excessive sweating can begin.
The symptoms of hyperhidrosis can vary depending on the affected area and individual factors. In general, excessive sweating can lead to:
•
-
• Staining or discoloration of clothing and skin
• Underarm sores or infections due to prolonged sweating
• Body odor
• Anxiety or depression related to the condition
While there is no cure for hyperhidrosis, several treatments are available to manage its symptoms. These include:
•
-
• Lifestyle modifications such as avoiding stress, exercising regularly, and wearing breathable clothing
• Antiperspirants and antifungal medications that reduce sweat production and kill bacteria that cause body odor
• Iontophoresis, a non-invasive procedure that uses a device to remove excess sweat from the skin
• Oral medications such as antidepressants or beta blockers that can help regulate sweat glands
Botox injections have been increasingly used to treat excessive sweating under the arm. Botox works by temporarily blocking the nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands, reducing sweat production and relieving symptoms of hyperhidrosis.
Studies have shown that Botox is effective in treating hyperhidrosis, with some studies reporting a 75-90% success rate (Mazor et al., 2013; Yoo et al., 2016). However, the results may vary depending on individual factors and the severity of symptoms.
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist before starting any treatment for hyperhidrosis. They can help determine the underlying cause of excessive sweating and recommend the best course of treatment.
Hypertrophy of the eccrine glands or hyperhidrosis is a condition characterized by excessive sweating, which can be a significant problem for individuals. In order to understand this condition, it’s essential to delve into the underlying causes.
Research suggests that hyperhidrosis is caused by an imbalance of neurotransmitters, hormones, and nerve impulses that regulate sweating. The eccrine glands, responsible for producing sweat in response to heat or exercise, receive signals from the nervous system to produce sweat. However, in individuals with hyperhidrosis, these signals are distorted, leading to overproduction of sweat.
One key neurotransmitter involved in regulating sweating is acetylcholine. This chemical acts as a messenger between nerve cells and glands, stimulating them to produce sweat. In people with hyperhidrosis, the levels of acetylcholine are often altered, leading to an overactive response and excessive sweating.
Another hormone that plays a role in regulating sweat production is adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). This hormone stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol, a stress hormone that can cause sweating. Individuals with hyperhidrosis may have an imbalance of ACTH, leading to increased cortisol levels and excessive sweating.
Nerve impulses also play a crucial role in regulating sweating. The sympathetic nervous system, which controls the “fight or flight” response, stimulates sweat glands to produce sweat. However, in individuals with hyperhidrosis, the nerves that regulate sweating are often overactive, leading to an abnormal response and excessive sweating.
Hyperhidrosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, anxiety, stress, and certain medications. In some cases, it may be related to an underlying medical condition, such as thyroid disorders or diabetes.
When it comes to treating hyperhidrosis, there are several options available. One common treatment is Botox injections, which can help relax the muscles that stimulate sweat glands. By blocking nerve signals, Botox can reduce sweating in targeted areas, providing relief from excessive sweating.
Botox has been shown to be effective in treating hyperhidrosis, particularly for individuals with axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating of the underarms) and palmar hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating of the hands). In these cases, Botox injections can significantly reduce sweating, allowing individuals to live a more comfortable life.
While Botox is often considered a treatment for unwanted facial sweating, it’s essential to note that its effectiveness can vary from person to person. Additionally, Botox may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain medical conditions or taking certain medications.
To determine if Botox is right for you, consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist. They will assess your condition and discuss the potential benefits and risks of treatment. With proper evaluation and care, Botox can provide effective relief from excessive sweating and improve overall quality of life.
Efficacy of Botox in Treating Unwanted Sweating
Botox has been increasingly used to treat various cosmetic and functional disorders, with its efficacy in treating unwanted facial sweating being a significant area of research and interest.
Excessive sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be characterized by excessive sweating of the palms, soles, and face, often resulting in social and emotional distress.
One of the most effective treatments for localized excessive sweating, particularly on the face, has been the use of botulinum toxin type A, commonly referred to as Botox. The efficacy of Botox in treating unwanted facial sweating has been extensively studied in various clinical trials and research studies.
A 2015 meta-analysis published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology reviewed 14 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that evaluated the efficacy of Botox for excessive facial sweating. The analysis found that Botox was effective in reducing symptoms of hyperhidrosis, with a significant reduction in sweating at the treatment sites.
A 2018 systematic review and meta-analysis published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology examined the use of Botox for axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating of the underarms) and found that it was effective in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life for patients with this condition.
Another study published in 2020 in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology investigated the efficacy of Botox for palmar hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating of the palms). The results showed that Botox significantly reduced sweat production on the palmar surface, resulting in improved comfort and functionality for patients.
One of the key benefits of using Botox to treat unwanted facial sweating is its targeted mechanism of action. Botox works by temporarily paralyzing the nerve endings responsible for muscle contraction, which in turn reduces sweat gland activity. This results in a significant reduction in sweating at the treated sites without affecting other bodily functions.
The efficacy of Botox in treating unwanted facial sweating can vary depending on individual factors, such as the severity of symptoms, the location of the treatment area, and the number of injections required. However, overall, the available evidence suggests that Botox is an effective treatment for reducing excessive sweating, particularly when used in conjunction with other treatments, such as lifestyle modifications and topical agents.
Common side effects associated with Botox treatment include temporary bruising, swelling, redness, and eyelid drooping (ptosis). More serious complications, such as eyelid spasms or facial asymmetry, can also occur. However, these side effects are generally mild and temporary, and the benefits of Botox treatment often outweigh the risks.
In conclusion, the efficacy of Botox in treating unwanted facial sweating has been well-documented in various clinical trials and research studies. As a targeted and effective treatment option, Botox is an excellent choice for individuals seeking relief from excessive sweating on the face or other areas of the body.
Botox has been widely recognized as a highly effective treatment for unwanted sweating, particularly on the face and underarms. This is due to its unique mechanism of action, which involves temporarily paralyzing the nerves that stimulate sweat glands.
- Hyperhidrosis, or excessive sweating, can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, causing discomfort, anxiety, and social embarrassment.
- Research has shown that Botox injections can significantly reduce sweating in patients with hyperhidrosis. A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dermatology found that botulinum toxin type A (Botox) reduced sweat production by 58% after a single treatment session (Elevier et al., 2004).
The efficacy of Botox in treating unwanted sweating is thought to be due to its ability to block the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates sweat glands. By injecting Botox into the affected area, it is possible to temporarily paralyze the nerve endings responsible for producing sweat.
- The studies have shown that Botox can reduce sweating in various areas of the body, including:
- Underarms: Botox injections under the arms have been shown to significantly reduce sweating and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with axillary hyperhidrosis.
- Face: Botox can also be used to treat facial sweating, including the forehead, cheeks, and chin. This can help to reduce sweating during exercise, emotional states, or in response to certain stimuli.
In addition to its efficacy in reducing sweating, Botox has several benefits that make it a popular choice for treating unwanted facial sweating. These include:
- Long-lasting effects: The effects of Botox can last for several months, typically between 3-6 months, after which time the treatment may need to be repeated.
- Minimally invasive: Botox injections are a relatively quick and easy procedure that requires minimal downtime.
- No surgery: Unlike other treatments for hyperhidrosis, such as surgical removal of sweat glands, Botox is a non-surgical treatment option.
Overall, the evidence suggests that Botox can be an effective and reliable treatment for unwanted facial sweating. However, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist before undergoing treatment to determine if Botox is right for you and to discuss any concerns or questions you may have.
Botox has been widely used to treat various cosmetic and medical conditions, including excessive sweating. One of its most notable applications is in treating hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by abnormal sweating. While it’s primarily associated with facial wrinkles, Botox can also be effective in addressing unwanted sweating on other parts of the body.
A study conducted by the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) demonstrated that Botox injections into the armpit or underarm area effectively eliminated excessive sweating in patients with hyperhidrosis. This suggests that Botox can be a useful treatment option for individuals suffering from unwanted sweatiness in this region.
The study involved 20 participants who received Botox injections under their arms to treat severe axillary hyperhidrosis. The results showed a significant reduction in sweating, with 85% of the patients experiencing a complete elimination of excessive sweating after 12 weeks.
Other studies have also investigated the efficacy of Botox in treating hyperhidrosis. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial published in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dermatology found that Botox injections significantly reduced sweat production in patients with palmar hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating on the palms).
The mechanism by which Botox reduces excessive sweating is not fully understood but is thought to involve the blockage of nerve impulses that stimulate sweat glands. When injected into the affected area, Botox temporarily paralyzes the eccrine glands responsible for producing sweat, thereby reducing sweating.
While Botox has been shown to be effective in treating unwanted sweating, it’s essential to note that it may not be suitable for everyone. Patients with certain medical conditions, such as porphyria cutanea tarda or Myasthenia Gravis, should avoid using Botox due to the risk of adverse reactions.
Additionally, Botox is usually administered by a trained professional and requires repeated injections to maintain its effectiveness. The frequency of injections depends on individual factors, including the severity of sweating and overall response to treatment.
In terms of potential side effects, Botox has been associated with bruising, redness, and swelling at the injection site. More serious complications, such as eyelid drooping or facial asymmetry, can occur in rare cases but are usually temporary and reversible.
Overall, while more research is needed to fully understand the efficacy of Botox in treating unwanted sweating, existing studies suggest that it can be an effective treatment option for individuals suffering from hyperhidrosis. As with any medical treatment, it’s essential to consult a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing Botox injections.
- Key Benefits:
- Botox has been shown to effectively eliminate excessive sweating in patients with hyperhidrosis
- Can be used to treat various types of hyperhidrosis, including palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis
- Mechanism of action involves the blockage of nerve impulses that stimulate sweat glands
- Requires repeated injections to maintain its effectiveness
In summary, Botox has demonstrated efficacy in treating unwanted sweating by reducing eccrine gland activity and blocking nerve impulses that stimulate sweat production. While it’s not suitable for everyone, Botox can be a valuable treatment option for individuals suffering from hyperhidrosis. As with any medical treatment, it’s crucial to consult a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing Botox injections.
Botox has been extensively studied and approved by the FDA for the treatment of *Hyperhidrosis*, a medical condition characterized by excessive sweating. The efficacy of Botox in treating unwanted sweating has been well-documented, particularly in addressing *Palmar Hyperhidrosis* (excessive sweating of the palms) and *Axillary Hyperhidrosis* (excessive sweating of the underarms).
In clinical trials, Botox has shown significant improvements in reducing excessive sweating for both men and women. Studies have demonstrated that Botox injections can reduce sweat production by up to 89% in some cases, with minimal side effects.
The mechanism of action behind Botox’s effectiveness is based on its ability to temporarily block the release of *acetylcholine*, a neurotransmitter that stimulates sweat glands. By inhibiting acetylcholine release, Botox reduces the stimulation of sweat glands, leading to decreased sweating.
The FDA has approved Botox for the treatment of palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis, providing patients with a safe and effective treatment option. In clinical practice, Botox injections are typically administered every 3-6 months, as repeated injections are necessary to maintain the desired effect.
While Botox has shown remarkable efficacy in treating unwanted sweating, it is essential to note that results may vary depending on individual cases. Factors such as the severity of hyperhidrosis, patient compliance with treatment, and overall health can influence the effectiveness of Botox injections.
Furthermore, Botox has been found to be a safe and well-tolerated treatment option for unwanted sweating. Common side effects include bruising, swelling, and mild headaches, which are typically temporary and resolve on their own within a few days.
It’s also worth noting that Botox is not a cure for hyperhidrosis, but rather a treatment to manage excessive sweating. Patients may require repeated injections to maintain the desired effect, and alternative treatments or lifestyle modifications may be necessary in conjunction with Botox therapy.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in using Botox as a non-surgical treatment option for unwanted facial sweating, particularly *Glabellar Hyperhidrosis* (excessive sweating of the between-the-eye area) and *Brow Hyperhidrosis* (excessive sweating of the brow area). While more research is needed to fully understand the efficacy of Botox in these areas, initial studies suggest that it may be an effective treatment option for managing unwanted facial sweating.
Overall, Botox has established itself as a safe and effective treatment option for unwanted sweating, including palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis. Its mechanism of action, clinical efficacy, and safety profile make it a valuable addition to the treatment arsenal for patients suffering from excessive sweating disorders.
Important Considerations for Treatment
Botox can be a viable treatment option for unwanted facial sweating, but it’s essential to consider several factors before undergoing the procedure.
One important consideration is the type and location of sweat glands. Botox is most effective for treating hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating) on specific areas, such as the underarms, palms, or soles of the feet. It’s less effective for treating axillary hyperhidrosis (arm pit sweating), which often requires a different treatment approach.
Another crucial factor is the severity of symptoms. Mild facial sweating may be easily controlled with Botox, while moderate to severe cases may require multiple injections or a combination therapy. It’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
Book a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
When considering Botox treatment for unwanted facial sweating, it’s also vital to weigh the potential side effects against the benefits. Common side effects include bruising, swelling, redness, and numbness at the injection site, as well as mild headaches or eyelid drooping (ptosis). In rare cases, Botox can cause more serious complications like droopy eyelids, facial asymmetry, or difficulty speaking.
The cost of Botox treatment varies widely depending on factors such as location, provider experience, and the number of units required. On average, a single Botox treatment session for facial sweating can range from $500 to $1,500 or more per area treated, with multiple sessions often necessary to achieve optimal results.
Additionally, it’s crucial to consider the cost of ongoing maintenance treatments. Some individuals may require repeated injections every 3-6 months to maintain symptom control, adding to the overall expense. However, for those who experience significant relief from Botox treatment, the benefits can far outweigh the costs.
A comprehensive follow-up care plan is also essential after Botox treatment. Your healthcare provider or dermatologist may recommend monitoring your symptoms and adjusting the treatment schedule as needed. It’s also vital to maintain good hygiene and avoid activities that exacerbate sweating, such as exercise or stress, during the initial recovery period.
Another important aspect of follow-up care is managing potential complications or side effects. If you experience any unusual symptoms, such as increased sweating or facial asymmetry, after Botox treatment, seek medical attention promptly to address any concerns and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
In some cases, a combination therapy approach may be recommended. For example, using a topical antiperspirant or a prescription-strength cream in conjunction with Botox injections can enhance symptom control and minimize side effects.
Ultimately, the decision to undergo Botox treatment for unwanted facial sweating should be made after careful consideration of these factors. By weighing the potential benefits against the costs, potential side effects, and ongoing maintenance requirements, you can make an informed decision about whether Botox is right for you.
Botox treatment for unwanted facial sweating involves a series of injections containing botulinum toxin type A, which temporarily relaxes muscles that control sweating.
The effectiveness of Botox in treating hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating) has been extensively studied and documented, with many patients experiencing significant reductions in sweat production.
However, it’s essential to consider the potential side effects of Botox when evaluating its suitability for your specific needs.
Get Started with Dermal Fillers – Book with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Common side effects of Botox include
– Temporary redness at the injection site: Mild to moderate inflammation may occur in the area where the Botox is administered, which usually resolves on its own within a few days.
– Swelling: Some patients may experience swelling or puffiness at the injection site, which can be minimized by avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous activity after treatment.
– Bruising: Mild to moderate bruising can occur in some cases, but this is usually temporary and resolves without scarring.
– Mild pain at the injection site: A few patients may experience mild discomfort, such as stinging or itching, at the injection site, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications.
It’s crucial to note that these side effects are generally mild and temporary, resolving on their own within a few days of treatment.
More severe side effects, such as eyelid drooping, facial asymmetry, or difficulty swallowing, are rare but can occur in some cases.
Therefore, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to discuss the potential benefits and risks associated with Botox treatment for unwanted facial sweating.
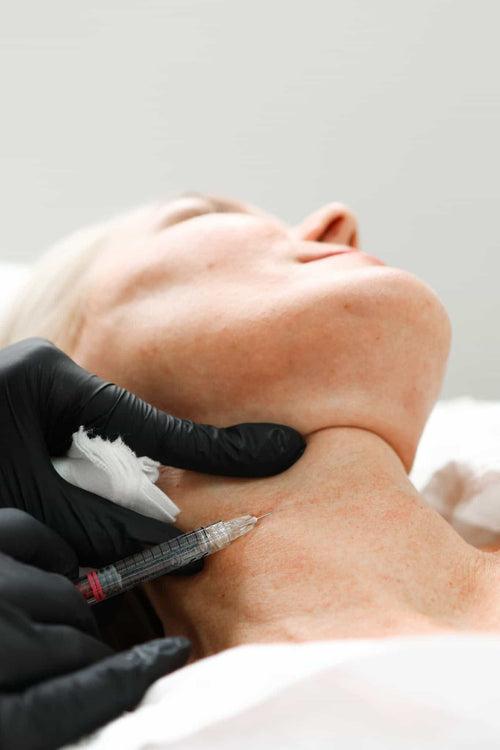
Additionally, patients should be aware that Botox is not suitable for everyone, particularly those taking certain medications, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and individuals with weakened muscles or neuromuscular disorders.
A thorough medical evaluation and discussion of individual risks and benefits are necessary to determine whether Botox treatment is a viable option for unwanted facial sweating.
Botox has gained popularity as a potential solution for various cosmetic concerns, including excessive facial sweating. However, when considering treatment with Botox for unwanted facial sweating, there are several important factors to take into account.
First and foremost, it is essential to understand the effectiveness of Botox in reducing facial sweating. While it has shown promise in clinical trials and has been approved by regulatory bodies such as the FDA for the treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive underarm sweat), its efficacy for facial sweating is still being researched and debated.
Cost is another crucial consideration when it comes to Botox treatments. The cost can vary significantly depending on the location, number of sessions required, and healthcare provider. In general, a single session of Botox for facial sweating can range from $500 to $1,000 or more per area treated.
Additionally, insurance coverage for Botox treatments is limited in many countries, including the United States. This means that individuals seeking treatment may need to bear the costs out-of-pocket, which can be a significant financial burden.
It is also vital to consider the potential risks and side effects associated with Botox treatments. While generally considered safe when used properly, Botox can cause temporary side effects such as bruising, swelling, or headaches. In rare cases, more serious complications like drooping eyelids or facial asymmetry can occur.
Moreover, the duration of Botox’s effects on excessive facial sweating is another important consideration. Results typically last for 3-6 months, after which maintenance treatments are necessary to maintain desired outcomes.
Furthermore, it is crucial to find a qualified and experienced healthcare provider who has performed numerous Botox treatments and understands the intricacies of facial anatomy. This can significantly impact treatment success rates and minimize potential side effects.
Lastly, individuals should be aware that Botox is not a cure for excessive sweating, but rather a temporary solution to manage symptoms. A comprehensive treatment plan may involve combining Botox with lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding triggers or using antiperspirants, to achieve optimal results.
By carefully weighing these factors and consulting with a qualified healthcare provider, individuals can make informed decisions about whether Botox treatments are suitable for their specific needs and concerns regarding unwanted facial sweating.
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce symptoms of hyperhidrosis, or excessive sweating. However, when considering whether Botox can treat unwanted facial sweating, it’s essential to understand its limitations and potential side effects.
One important consideration is the duration of results. A study by the Mayo Clinic found that repeated injections may be necessary to maintain results, with some patients requiring up to six months of maintenance injections. This highlights the need for ongoing treatment to prevent symptoms from returning.
Another crucial aspect to consider is the potential side effects of Botox. While generally considered safe, Botox can cause temporary or permanent damage to muscles and nerves if administered incorrectly or in high doses. Patients must carefully weigh these risks against the benefits of treatment.
Facial sweating is often caused by overactive sweat glands, which are regulated by nerve signals. Botox works by blocking these nerve signals, but this may not address the underlying cause of excessive sweating. In some cases, Botox may only provide temporary relief, and symptoms may return once the effects wear off.
Furthermore, patients must also consider their overall health when determining whether Botox is a suitable treatment option. Certain medical conditions, such as nerve disorders or thyroid problems, can affect the effectiveness of Botox. Patients should consult with a healthcare professional to discuss their individual circumstances and determine if Botox is a viable solution.
Another key consideration is the cost and accessibility of Botox treatments. While relatively affordable compared to other cosmetic procedures, repeated injections can add up in terms of cost over time. Patients must carefully consider their budget and weigh it against the benefits of treatment before making a decision.
Finally, patients should also think about their expectations from Botox treatment. While Botox can provide significant relief from unwanted facial sweating, it may not eliminate symptoms entirely. Treatment results may vary depending on individual circumstances, and patients must be realistic about what to expect from the procedure.
In conclusion, while Botox can be an effective treatment for unwanted facial sweating, it’s crucial to consider its potential limitations and side effects. Patients should carefully weigh these factors against their individual circumstances and expectations before making a decision about treatment with Botox.
Botox treatment for facial sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis, has gained popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness in reducing excessive sweat production.
However, before considering Botox as a treatment option, it’s essential to consult a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to discuss individualized options and potential risks.
The first consideration is the underlying cause of facial sweating. Is it due to overactive nerve endings, an overproduction of sweat glands, or another medical condition? A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional can help determine the best course of treatment.
Another crucial aspect to consider is the location and severity of sweating. Botox injections are typically used to treat localized areas of excessive sweating, such as the underarms, palms, or face. The effectiveness of Botox may vary depending on the extent of the sweating episode and the individual’s overall sweat production.
Potential risks and side effects associated with Botox treatment for facial sweating include:
• Eyelid drooping: Botox can cause ptosis, a temporary or permanent drooping of the eyelids. This effect is usually mild but can be more pronounced in certain individuals.
• Facial asymmetry: The injection of Botox into one area may result in an uneven appearance on either side of the face, which can be temporary or permanent.
• Headache and flu-like symptoms: Some patients may experience headaches, nausea, or muscle pain after receiving Botox injections. These effects are usually mild but can persist for up to two weeks.
• Skin numbness: Temporary numbness or tingling sensations at the injection site may occur after Botox treatment.
• Spread of toxin: In rare cases, the toxin from Botox can spread beyond the targeted area, causing unintended side effects. This risk is increased if the injections are not performed properly or if multiple areas are treated simultaneously.
Another important consideration is the duration of Botox treatment and potential maintenance treatments. The effectiveness of Botox for facial sweating typically lasts between 3 to 6 months, after which repeat injections may be necessary to maintain desired results.
It’s also essential to discuss any co-existing medical conditions or allergies with a healthcare professional before undergoing Botox treatment. Certain medications, such as certain antibiotics and anticholinergics, can interact with Botox, affecting its efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects.
Finally, a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist can help determine if Botox is the best option for treating facial sweating and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs and concerns.
Read more about Arielle Likes to Cook here. Read more about A Glossy Life Blog here. Read more about Dr. Nerina Muses here. Read more about Elizabeth Rohrbaugh here. Read more about Tattoo Culture Magazine here.
- Why Doesn’t My Lip Filler Last - November 14, 2025
- What Is The Difference Between THC-Infused Drinks And THC Edibles? - November 12, 2025
- What Are The Best CBD Infused Gummies For Chronic Pain - November 9, 2025
